The manipulators present in the industry today use, mostly, of direct current servomotors. Despite the ease of modeling and control of this type of machine, its maintenance is costly due to the quantity of components and the mechanical contact of its parts. The three-phase induction motors (MIT) of the "Squirrel cage" type, in turn are simple construction engines, cheaper and easy maintenance, plus a greater robustness compared to other types of electrical machines, its use in the industry is quite Widespread. The GPAR has researches in industrial robotics as the present project, involving areas of identification of systems, embedded systems, control, computational intelligence and image processing.
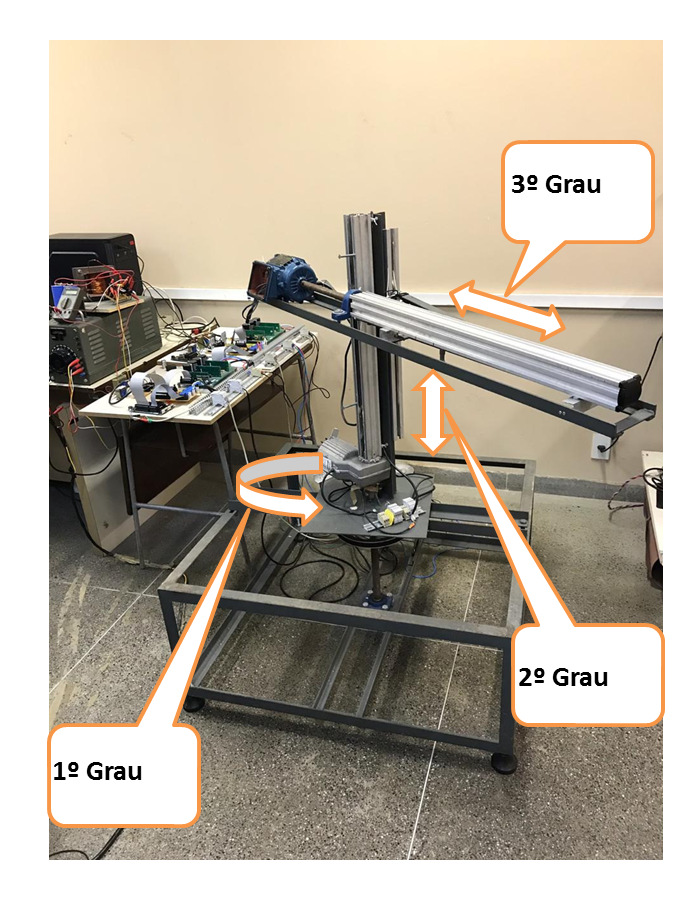
The search handler is cylindrical type and has 3 degrees of freedom, the first degree is the basis that has rotating movements, the second degree is linear that is the trunk that makes the movements vertically, the third degree is what makes the movements horizontally. The handler has the joints driven with three-phase induction motors.
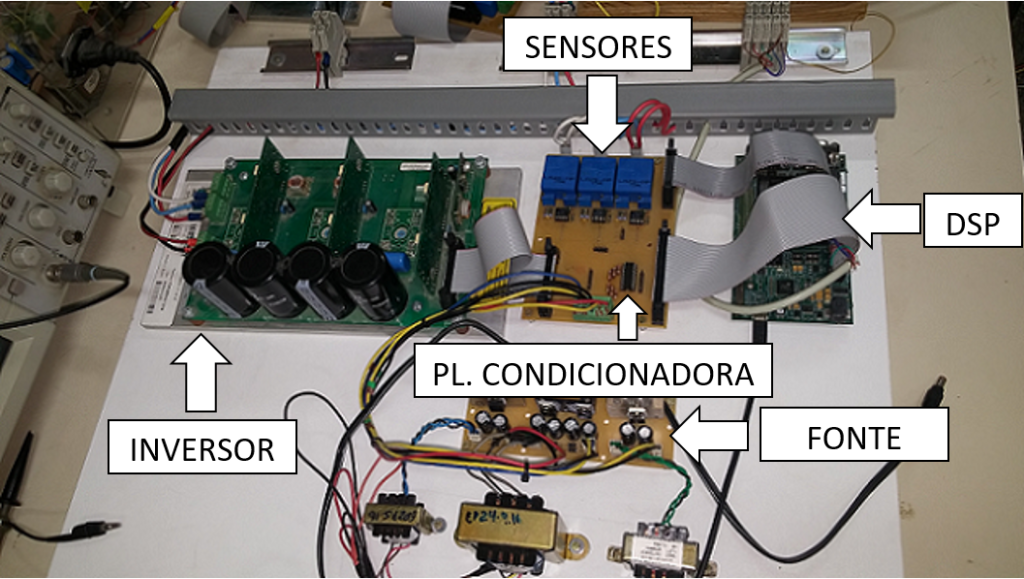
For the actuation of the Manipulator it was necessary to use a DSP (digital signal processor) microcontroller of Texas instruments. The main advantage of it is that in addition to high performance is the ability to perform 150 MPIS (million instructions per second), intrinsic support for vector spatial modulation, SVPWM. The programming interface is CCS, which will be implemented in C, with a very broad community (L. R. REBOUÇAS, 2015).
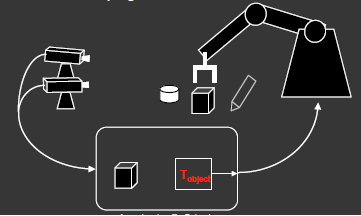
The work also has an image processing part to assist in performing tasks with a camera on the outside. A Sipeed Maix Bit chip that has the 400 Mega-hertz, dual core and 64-bit configuration will be used, along with a MaixPy (MicroPython) tool using the Yolo image recognition system (You Only Look Once). The final plan sketch as an example would look like the Figure below.
Jobs Accepted for publication and published until September 2019.
- D. A. Souza, L. L. N. Dos Reis, J. G. Batista, J. R. Costa, A. B. S. Junior, J. P. B. Araújo, A. P. S. Braga. Nonlinear Identification of a Robotic Arm using Machine Learning Techniques. 7th World Conference on Information Systems and Technologies, La Toja Island, Galicia, Spain, 2019; Published
- D. A. Souza, L. L. N. Dos Reis, J. G. Batista, J. R. Costa, A. B. S. Junior, J. P. B. Araújo, A. P. S. Braga. Nonlinear Identification of a Robotic Arm. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, 2019; (Published);
- D. A. Souza et al. Identificação With a recursive minimum square variation applied to a Robotic manipulator. SBAI, Ouro Preto-MG, 2019. (Accepted for publication);
- J. G. Batista et al. Modeling Dynamic and simulation of a PID and LQR controller for a Cylindrical manipulator. SBAI Ouro Preto-MG, 2019. (Accepted for publication);
- D. A. Souza et al. Identification Of the Recursive Least Squares with RMO applied to a Robotic Manipulator. Artificial Intelligence for Industries, Laguna Hills, California USA, 2019. (Accepted for publication).
- J. G. Batista et al. Performance Comparison Between the PID and LQR Controllers Applied to a Robotic Manipulator Joint. Lisbon, Portugal. IECON, 2019. (Accepted for publication).
Members
Laurinda Lucia Nogueira dos Reis – Dr.
Antonio Barbosa de Souza Júnior – Dr.
Darielson, Alabama Araújo de Souza-PhD student.
Josiah Guimarães Batista – PhD student.
José Nogueira do Nascimento Júnior – Master's student.
José Raimundo de Oliveira Júnior-Undergraduate student.